About Us
Turku Research Institute for Learning Analytics (TRILA) develops digital teaching tools and researches their effects on learning. Our work is divided into three fields: the research of digital teaching and learning analytics, advancing the materials, tools and practices used in teaching and guidance, and finally, the societal impact in the use of digital tools and analytics.
A concrete example of our work is the digital learning platform ViLLE, which is widely used in schools, universities, and universities of applied sciences. Research shows that learning based on the ViLLE platform is linked to better results in learning, more effective study guidance, and a higher number of completed studies.
The Institute is part of University of Turku, and its operation is linked to the university’s strategy as a developer of better teaching.
Learning Analytics
The goal of learning analytics is to offer tools and methods for monitoring studies and predicting difficulties in learning. Guidance counselling and automating teaching and learning aids are of particular interest in the field. Through these means we seek tested, justified, and ethical ways to enhance learning, teaching, study guidance, and administrative processes.
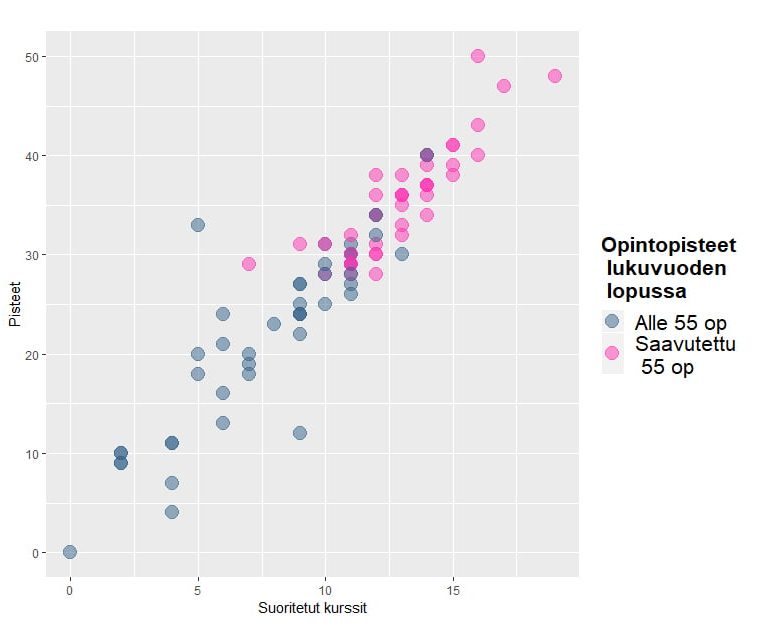
A typical approach to creating tools in learning analytics is the development of predictive models from existing data. For example, by examining students’ yearly accumulation of study points it is possible to predict the accumulation of upcoming years. This enables early intervention when corrective measures are still useful in preventing problems.
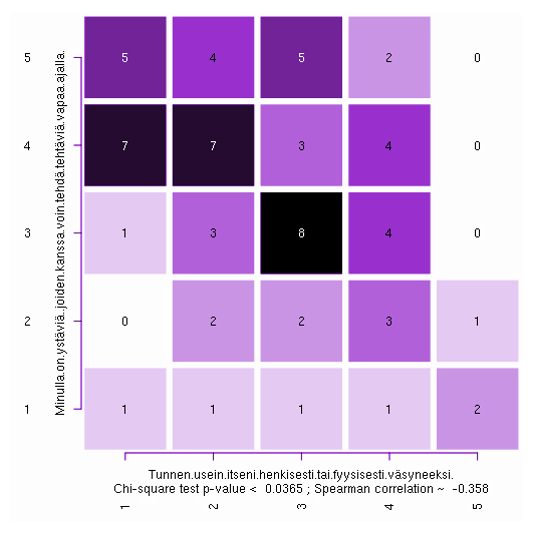
Questionnaires can be powerful tools in gathering data for learning analytics, especially if it can be combined with other data (such as that gained from learning platforms or sensors). Still, questionnaires alone can also yield important results. The attached picture combines two questions picked from a questionnaire measuring study habits of students.
As we can see, students who report having friends they can complete assignments with also report significantly fewer occasions of feeling mentally or physically tired. Therefore, it is clear that formation of friend groups among students should be facilitated.
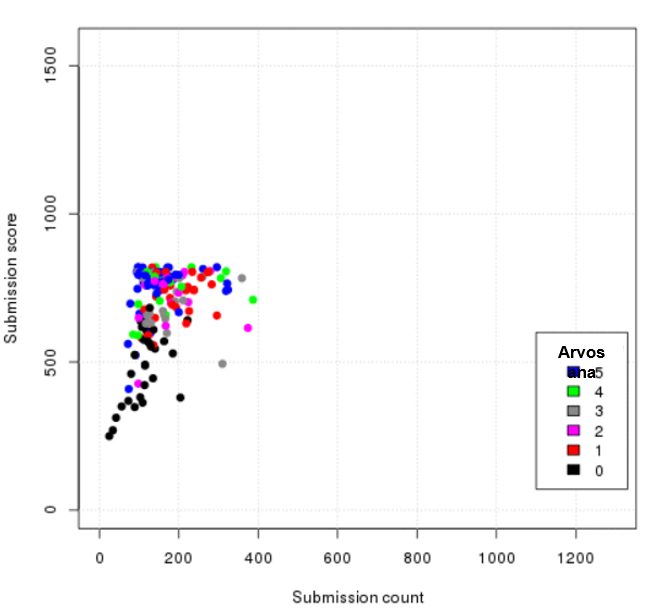
Continuous assessment and comprehensive collection of course achievements enables the development of a model that can be used to predict course outcomes. The picture shows achievements of the first two weeks of an eight-week course. Each dot represents a student enrolled in the course. The dots are color-coded based on the final grade achieved. What is notable here is that the model can predict 80% of students who are going to fail the course during the first two weeks.
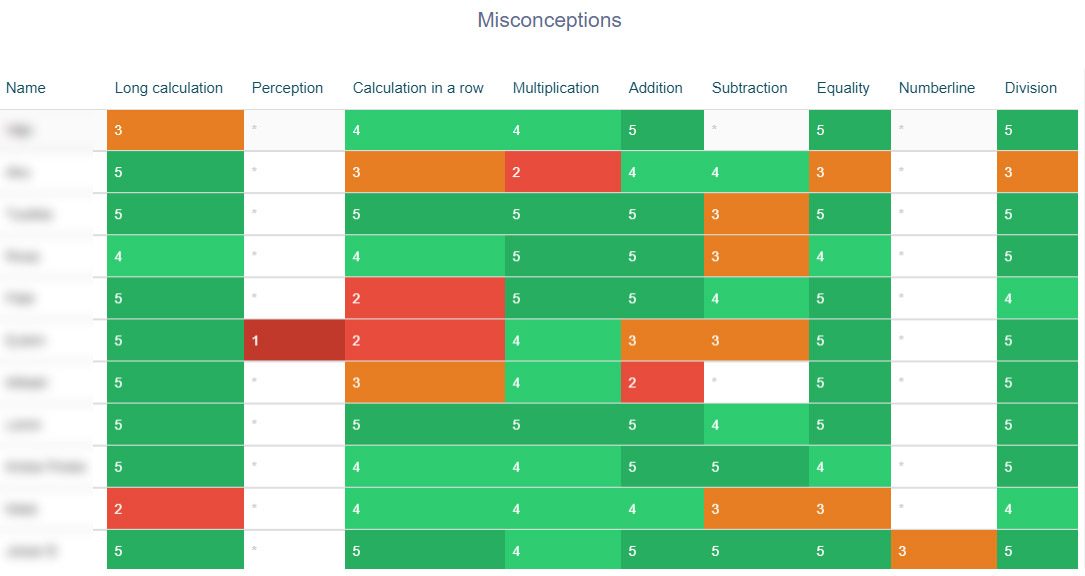
ViLLE automatically recognizes students’ learning misconceptions in mathematics based on the information collected from their submissions.
A study showed that the algorithms of ViLLE predict learning misconceptions as effectively as a widely-used pen and paper test. The difference is that automatic analytics enables real time viewing of information without a separate test.
Research
Our research is focused on different aspects of digital learning and learning analytics. Currently, some of our key areas of research are:
Our research aims to support both educators and students by responding to societal and pedagogical needs. For example, information gained from research is used to develop the ViLLE Learning Platform to better suit the needs of its users. In the end, we aim to create knowledge that serves the educational field as a whole. You can explore our studies below.
If you would like to suggest research collaboration, please contact us!
Publications
Journal of Educational Technology Systems (2020)